In this blog, I aim to simplify the concepts of iterators and aggregators within Make.com. By understanding how data flows in this platform, you’ll be able to enhance your automation processes effectively.
Overview of Iterators and Aggregators
Iterators and aggregators play a crucial role in handling data within Make.com. An iterator processes each item in a bundle individually, while an aggregator combines multiple bundles into one. Understanding how these elements work helps streamline your automation tasks.
When you pull data from sources like Google Sheets, each row is treated as a bundle. An iterator allows you to process each row separately, executing actions based on the data it contains. This is useful when you want to send individual messages or perform actions for each item.
On the other hand, aggregators allow you to consolidate data. Instead of sending multiple messages for each bundle, you can combine that data into a single output. This is particularly efficient when dealing with large sets of data, as it reduces API calls and streamlines operations.
Bundles in Make.com
In Make.com, a bundle represents a single data item, like a row in a Google Sheet. Each bundle can contain multiple fields, such as customer names and order totals. When you set up your scenario, each bundle is processed one at a time, allowing for precise control over the data flow.
For example, if you were to pull customer orders from a Google Sheet, each order would be a separate bundle. By using an iterator, you can take action on each order individually. This could mean sending a notification or updating a database for every order.
Combining Data with Aggregators
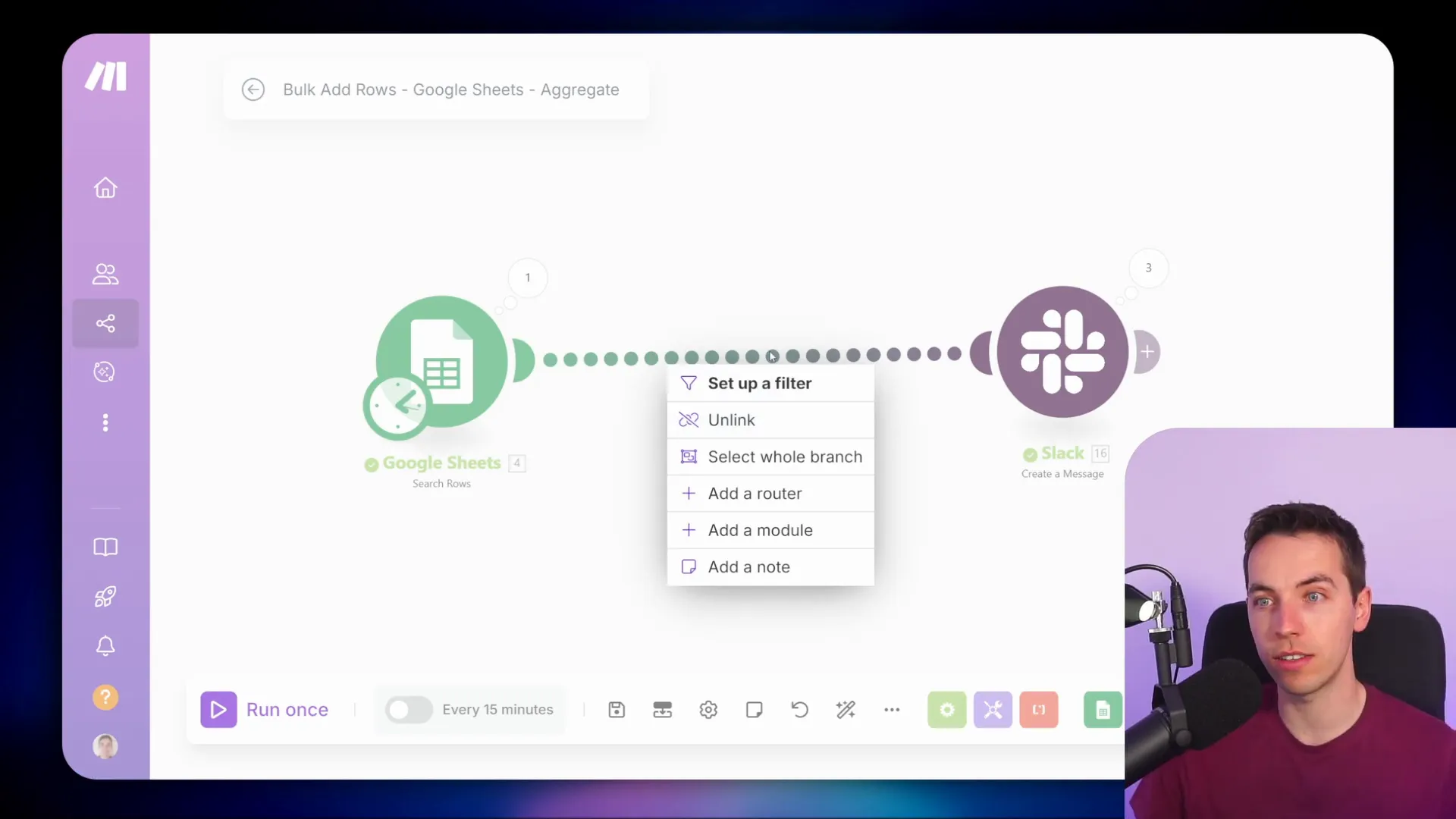
Aggregators are essential when you want to merge data from multiple bundles into a single output. This is particularly useful for generating summary reports or sending consolidated messages. Instead of sending a message for each order, you can use an aggregator to combine all orders into one message.
Using an aggregator not only simplifies your output but also reduces the number of operations used in your scenario. For instance, when you use a text aggregator, it can take all the individual order details and compile them into a single string. This approach saves on resources and makes your workflows more efficient.
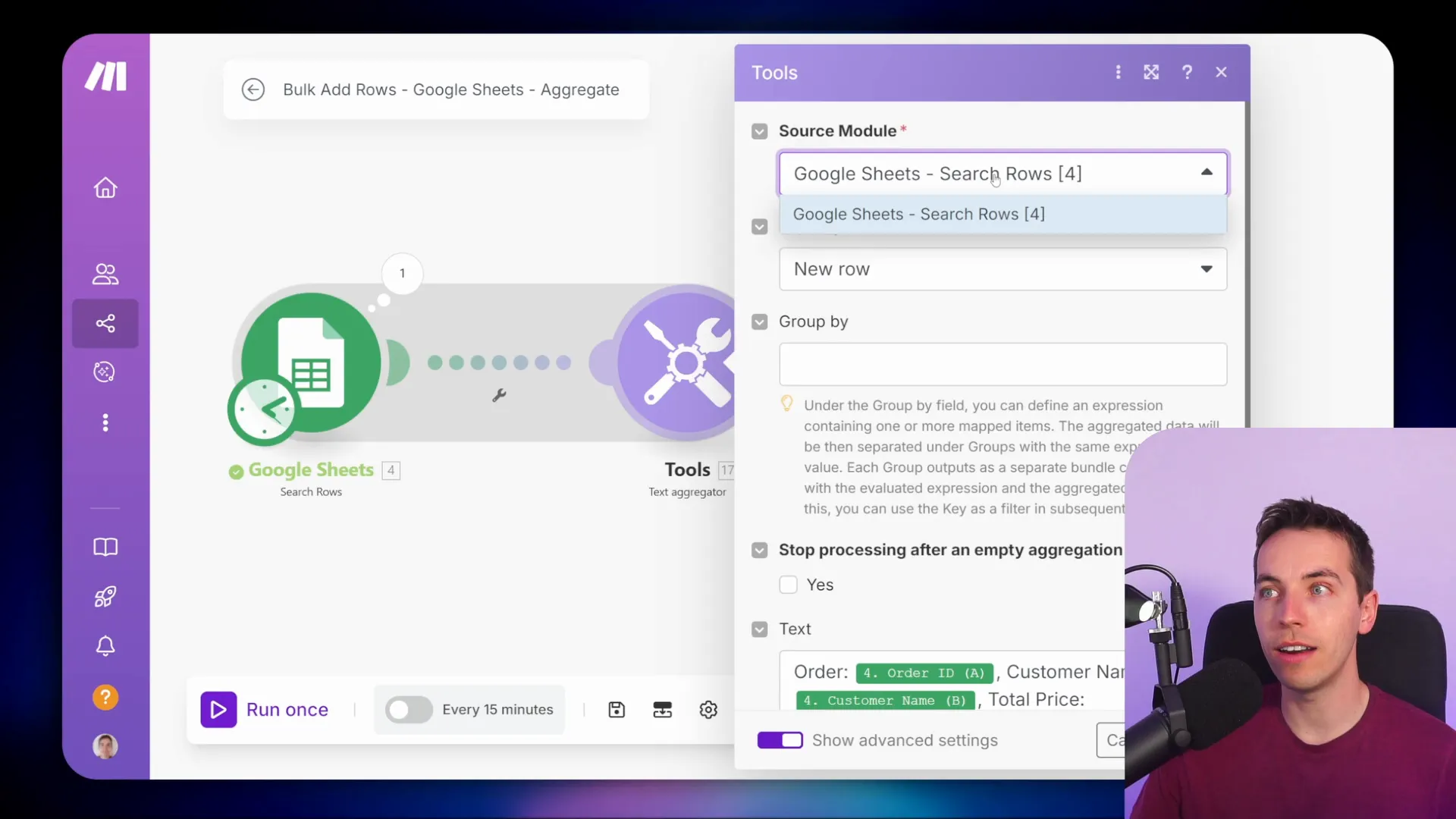
Using the Text Aggregator
The text aggregator is one of the simplest aggregators to understand. It combines multiple strings into one long text output. To use it, you simply select the data you want to combine and specify how you want it formatted, such as separating values by commas or new lines.
For example, if you want to send a summary of orders in Slack, you can set up a text aggregator to compile customer names and total prices. This way, instead of sending separate messages for each order, you get a single message that summarizes all the information.
Practical Use Cases for Aggregators
Aggregators have a variety of practical applications in automation. One common use case is generating daily summaries of orders. By setting up a scenario that runs at the end of each day, you can pull all orders from that day and aggregate them into one message to send to your team.
Another example is using a numeric aggregator to calculate totals. If you want to know the total sales for the day, you can set up a numeric aggregator to sum the order values. This gives you a quick overview of performance without needing to manually compile the data.
Numeric Aggregator
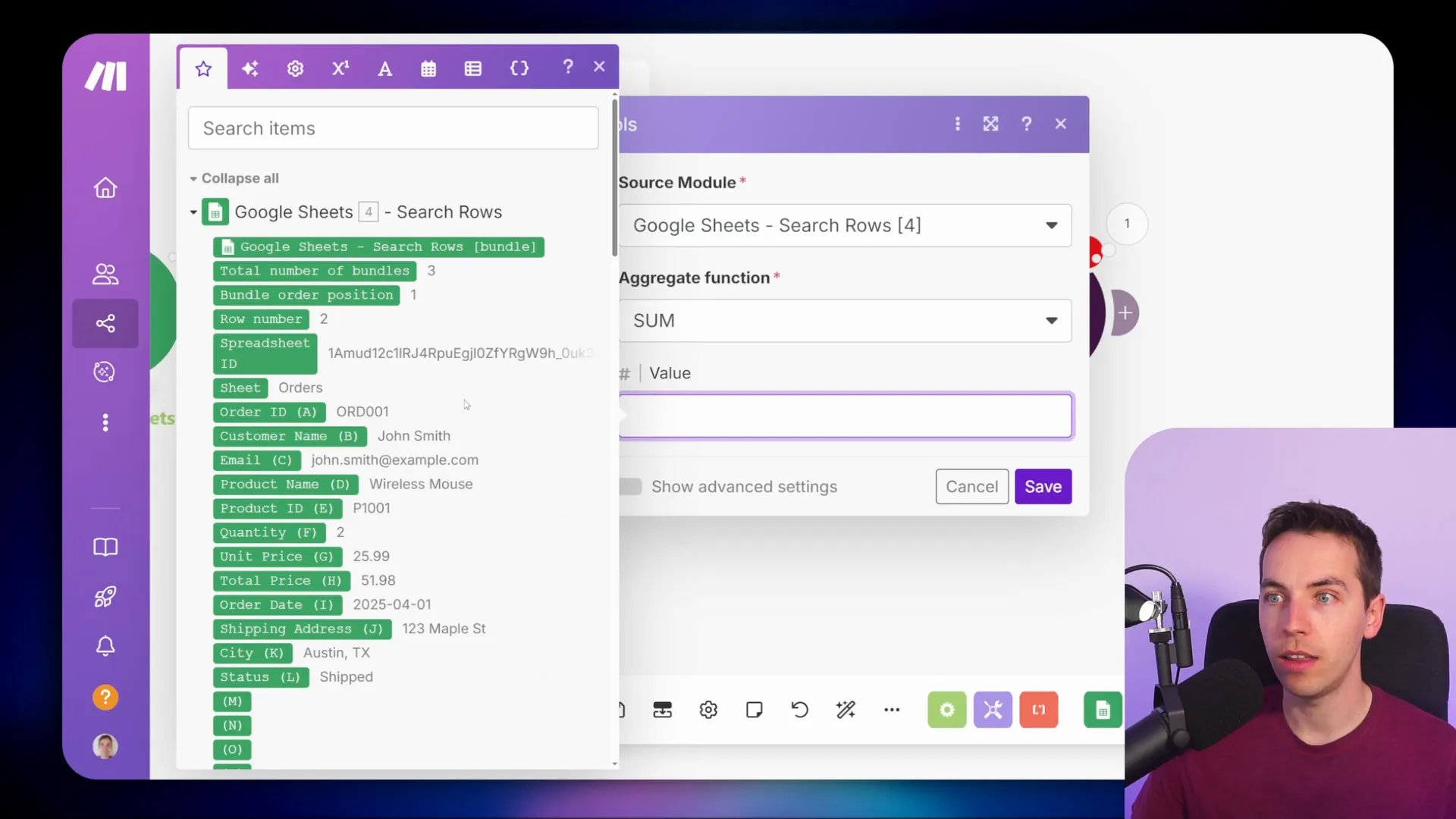
The numeric aggregator is a powerful tool that allows you to perform calculations on a series of numeric values. This can be particularly useful when you want to summarize data, such as calculating total sales or averages from a set of orders.
To set it up, I usually add a module and navigate to the tools section. From there, I select the numeric aggregator. You can choose various functions like sum, average, or count. For example, if I want to calculate the total price of all orders, I would select the sum function and map the total price field from my data source.
Once I save this configuration and run the scenario, it aggregates the values and provides a single output. This output can then be used in subsequent actions, like sending a summary message to a team channel.
Understanding Arrays and Collections
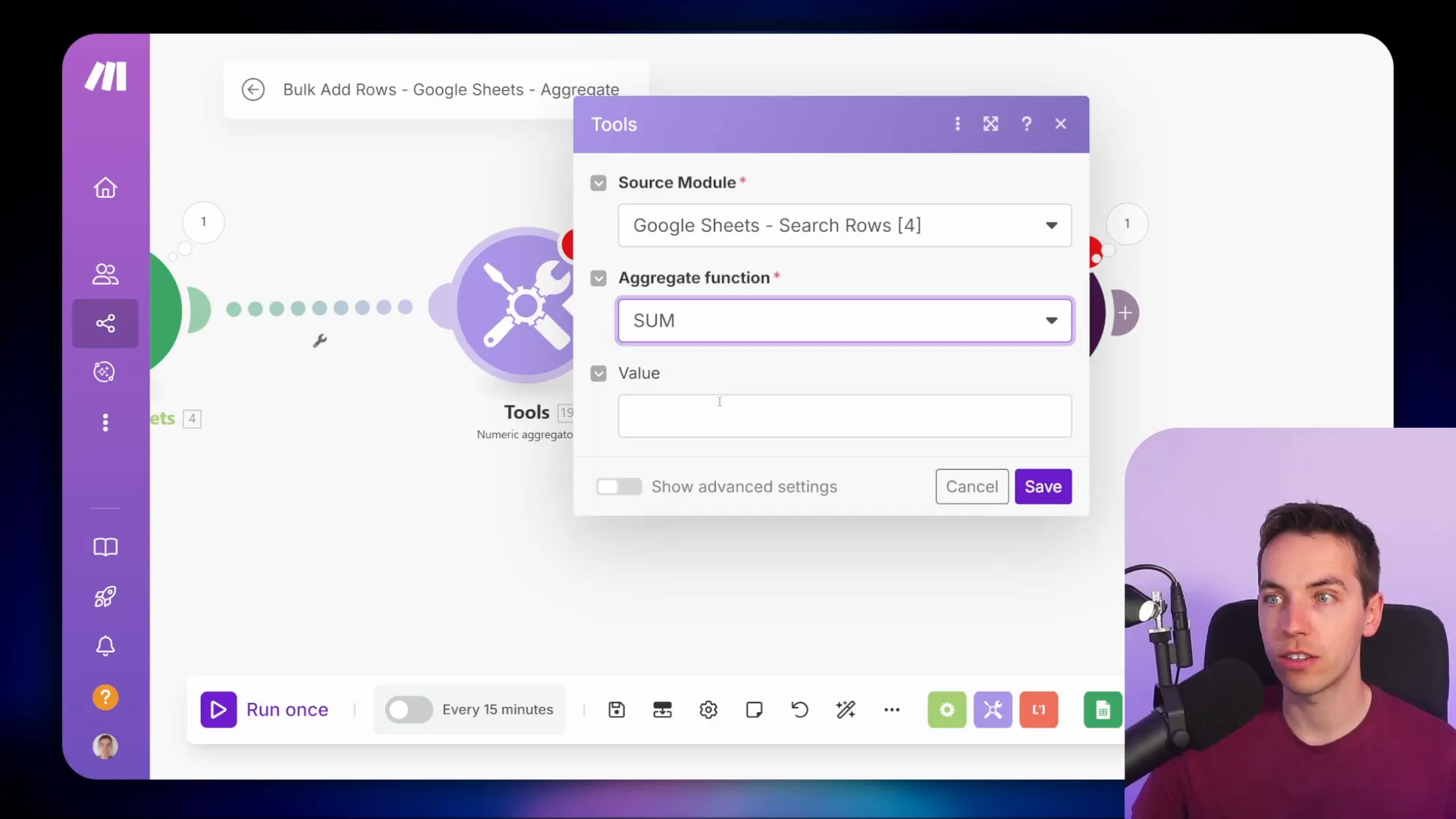
Arrays and collections are essential data structures in Make.com that allow you to handle multiple items efficiently. An array is essentially a numbered list of items, while a collection groups individual data items together.
For instance, when dealing with emails, an array might contain multiple attachments. Each attachment is indexed, allowing for easy iteration. Collections, on the other hand, can represent multiple fields or data items related to a single entity, like a customer or order.
Understanding these structures is crucial when you want to manipulate data effectively, especially when using iterators to process each item in a flow.
Using Iterators
Iterators are vital for processing each item in a bundle. They allow you to loop through arrays or collections, performing the same action on each item. To use an iterator, you first select the array or collection you want to iterate over.
For example, if I have an array of email attachments, I can set up an iterator to upload each attachment to Google Drive. By mapping the file name and data from the iterator, I ensure each attachment gets processed correctly.
This approach simplifies workflows, especially when dealing with multiple items, as it maintains a clear flow of data and operations.
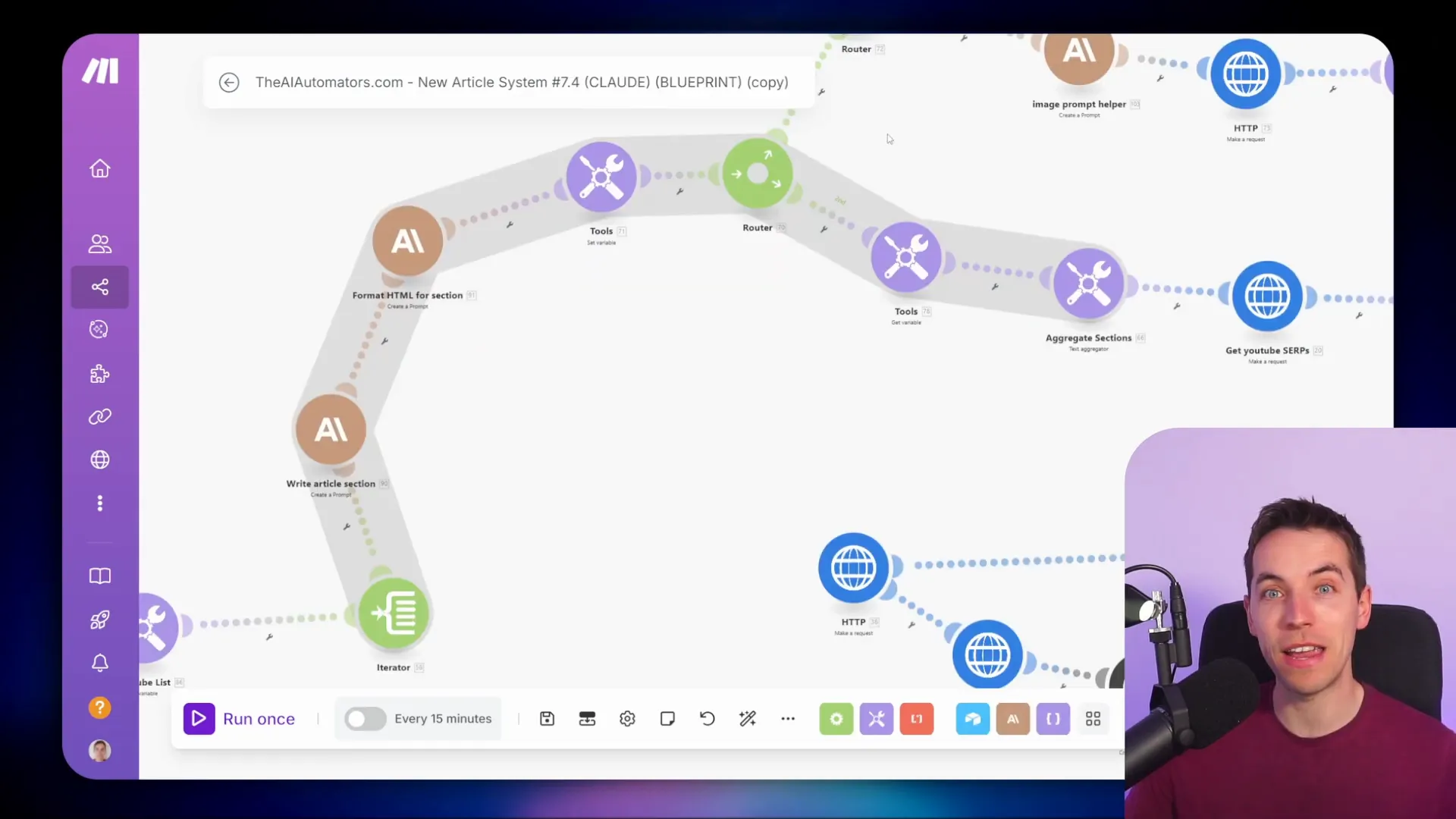
Converging Bundles with Aggregators: Blog Post Example
In a blogging context, I often use iterators and aggregators to streamline article creation. For instance, I can create an outline for a blog post and then iterate through each section to generate content.
After writing all the sections, I use an aggregator to combine them into a single article. This ensures that the final output is cohesive and ready for publishing.
This method not only saves time but also minimizes errors, as I can focus on creating content without worrying about the final formatting until the end.
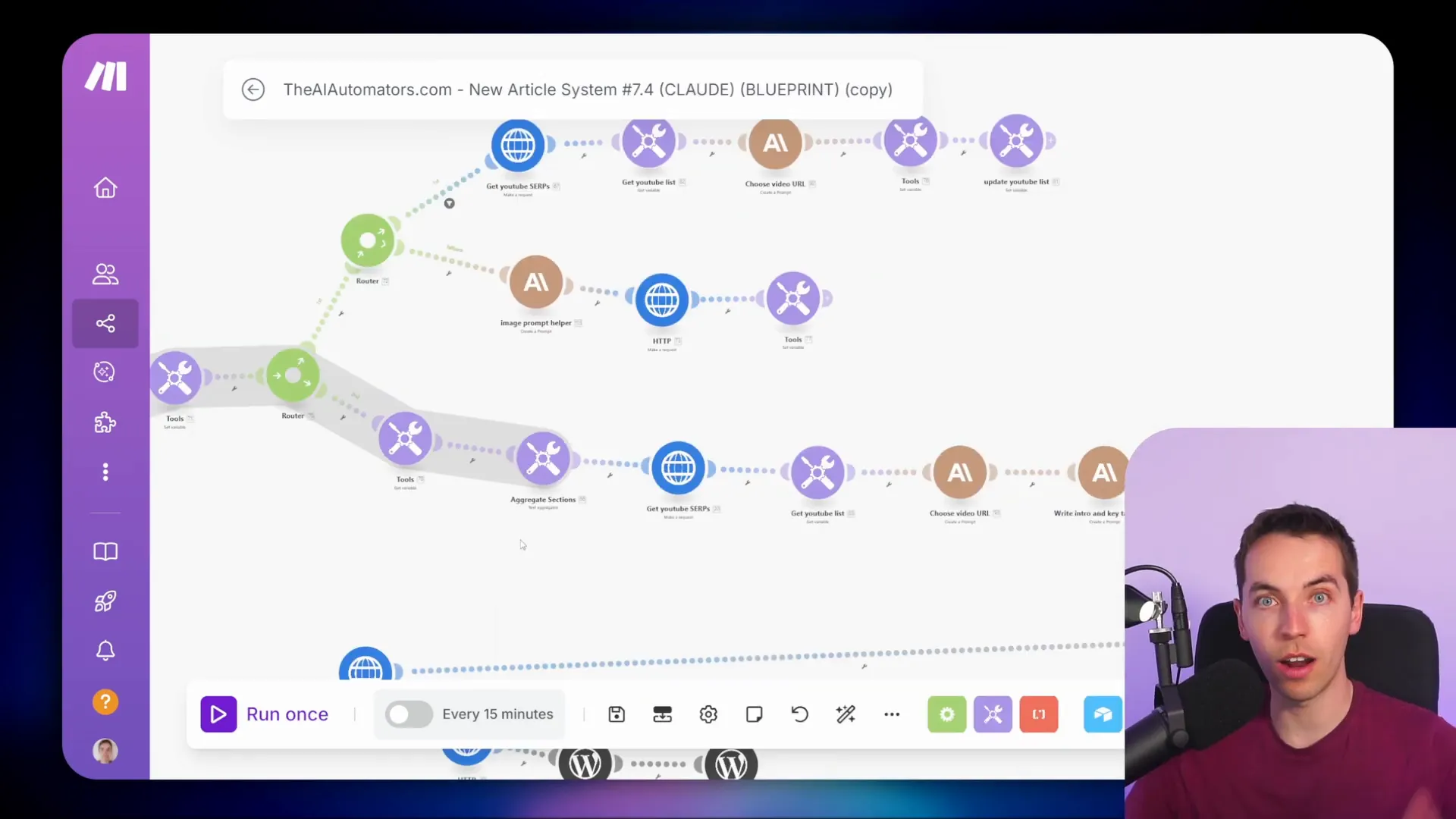
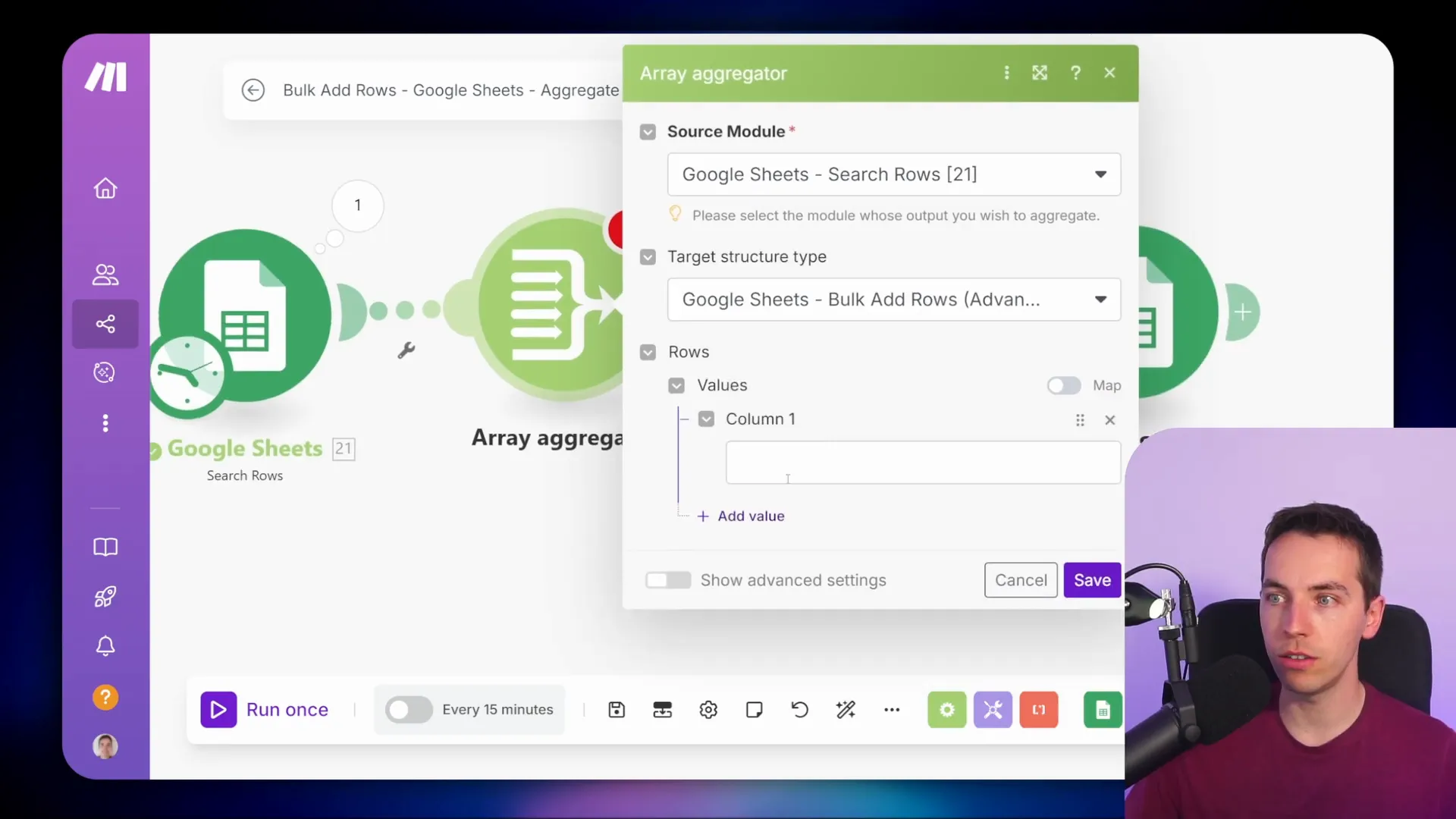
Efficient Data Handling with Array Aggregators
Array aggregators take efficiency to the next level by allowing you to combine multiple bundles into one array. This is particularly useful when you want to perform bulk operations, such as adding multiple rows to a Google Sheet.
By using an array aggregator, I can gather all relevant data from various bundles and prepare it for a single operation. This reduces the number of API calls needed, making the process much more efficient.
For example, instead of adding each order to a Google Sheet individually, I can aggregate all order details into one array and then perform a bulk add operation. This not only speeds up the workflow but also conserves resources and minimizes costs.